Atopic Dermatitis Eczema is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. Also known simply as eczema, it is characterized by inflamed, itchy, and dry skin that can be both uncomfortable and distressing. This chronic condition often goes through periods of flare-ups and remission, making it important to understand its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Atopic Dermatitis Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes inflamed, itchy, and dry skin.
- It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for Atopic Dermatitis Eczema.
- By identifying the triggers and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
- Treatment options for Atopic Dermatitis Eczema include medications, topical creams, and lifestyle changes.
- Consulting a dermatologist is essential for accurate diagnosis and comprehensive treatment plans.
Understanding the Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema
Atopic Dermatitis Eczema is a chronic condition that affects the skin, causing inflammation, itching, and discomfort. It is important to recognize and understand the symptoms associated with this condition to effectively manage and seek appropriate treatment.
The most common symptom of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema is the presence of a red, itchy rash on the skin. This rash can appear on any part of the body, but it is most commonly found on the face, neck, elbows, knees, and ankles. The skin affected by the rash may also become dry, scaly, and thickened.
In addition to the visible rash, individuals with Atopic Dermatitis Eczema may experience intense itching, which can worsen at night. Scratching the affected areas can lead to skin damage, infections, and increased inflammation. Persistent scratching can also cause the rash to spread to other parts of the body, exacerbating the symptoms.
Other symptoms associated with Atopic Dermatitis Eczema may include:
- Blisters or oozing lesions on the skin
- Skin discoloration or hyperpigmentation
- Swelling, especially around the eyes
- Sensitive and reactive skin
- Dry and cracked skin that may bleed
- Sleep disturbances due to itchiness and discomfort
It is important to note that the severity and frequency of symptoms may vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild, occasional flare-ups, while others may have more persistent and severe symptoms.
“Living with Atopic Dermatitis Eczema can be challenging due to the uncomfortable symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.” – Dr. Sarah Johnson, Dermatologist
Causes and Risk Factors of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema
In this section, we will explore the various causes and risk factors that contribute to the development of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema. Understanding these factors is crucial for taking preventive measures and effectively managing the condition.
Genetic Predisposition:
Atopic Dermatitis Eczema has a strong genetic component, making it more likely for individuals with a family history of the condition to develop it themselves. Specific gene mutations are often associated with an increased risk of developing Atopic Dermatitis Eczema.
Immune System Dysfunction:
A compromised immune system plays a significant role in the development of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema. In individuals with the condition, the immune response is overactive, leading to inflammation and skin irritation. This immune dysfunction can be triggered by various factors, including environmental allergens and stress.
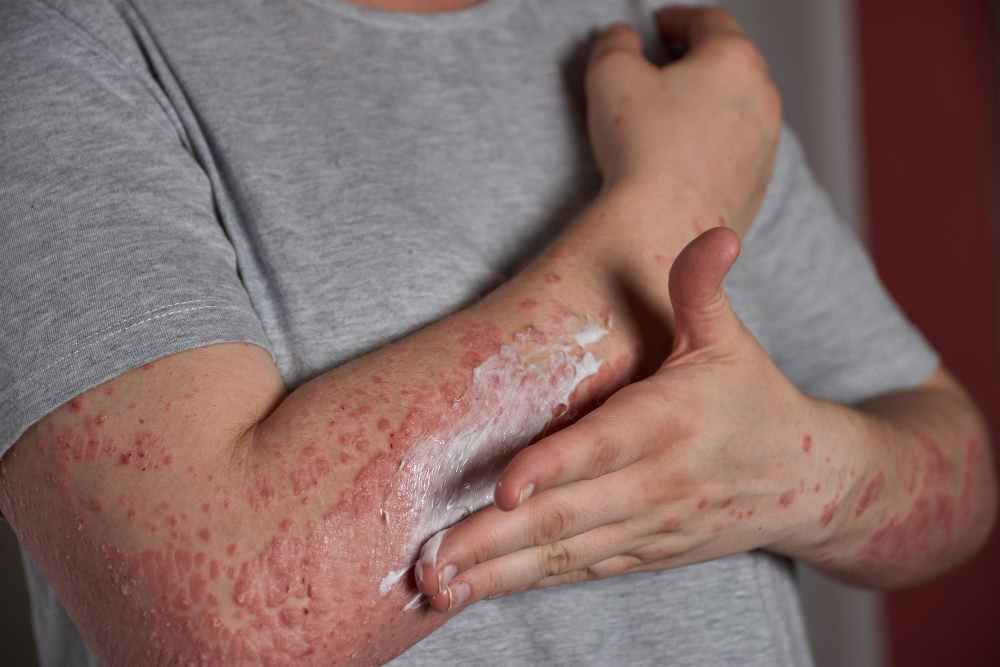
Environmental Factors:
Exposure to certain environmental triggers can worsen the symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema. Common irritants include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold, and certain chemicals found in soaps, detergents, and skincare products. Additionally, extreme weather conditions and low humidity levels can also exacerbate the condition.
Food Allergies:
Some individuals may have allergies to certain foods, such as dairy products, eggs, soy, wheat, and nuts. Consumption of these allergenic foods can trigger or worsen the symptoms of the condition. Identifying and avoiding these trigger foods can help manage Atopic Dermatitis Eczema effectively.
Stress and Emotional Factors:
Stress and emotional factors can have a significant impact on the severity of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema symptoms. High levels of stress can weaken the immune system and trigger inflammation, leading to flare-ups. Emotional factors like anxiety and depression can also contribute to the worsening of symptoms.
| Possible Causes of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema | Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Family history of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema |
| Impaired Immune System | Environmental allergens |
| Environmental Triggers | Dust mites, pet dander, pollen, chemicals |
| Food Allergies | Allergenic foods |
| Stress and Emotional Factors | High stress levels, anxiety, depression |
By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with Atopic Dermatitis Eczema, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize triggers, effectively manage the condition, and improve their quality of life.
Management and Treatment
In this section, we will discuss effective strategies for managing and treating Atopic Dermatitis Eczema. Both medical and lifestyle approaches play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms, reducing flare-ups, and improving the overall quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments typically focus on managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Several options are available, including:
- Topical corticosteroids: **These** are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and itchiness associated with flare-ups.

- Topical calcineurin inhibitors: **These** medications help manage symptoms by suppressing the immune response in the affected areas.
- Antihistamines: These can be used to relieve itching and improve sleep..
- For severe cases, doctors prescribe oral or injectable immunosuppressants to manage symptoms.
Lifestyle Approaches
Adopting certain lifestyle approaches can significantly contribute to the management of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema. Here are some recommended practices:
- Maintain a regular skincare routine: Use gentle cleansers and moisturizers recommended by dermatologists to keep the skin hydrated and minimize irritation.
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid factors that trigger flare-ups, such as certain fabrics, extreme temperatures, and allergens.
- Wear comfortable clothing: Opt for soft, breathable fabrics and avoid tight-fitting garments that can further irritate the skin.
- Manage stress: Stress can worsen symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis Eczema</b>, so incorporating stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or exercise can be beneficial.
- Keep nails short: Short nails help prevent accidental scratching and minimize potential skin damage.
- Moisturize regularly: Applying a fragrance-free moisturizer helps keep the skin hydrated and reduces dryness, which is often a trigger for flare-ups.
Comparing Medical and Lifestyle Approaches
| Medical Approaches | Lifestyle Approaches |
|---|---|
| Focuses on managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups through medications. | Emphasizes practices that minimize triggers and promote overall skin health. |
| May involve the use of topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, antihistamines, or systemic medications. | Includes maintaining a regular skincare routine, avoiding triggers, managing stress, keeping nails short, and moisturizing regularly. |
| Requires medical supervision and prescription. | Can be incorporated into daily life as self-care practices. |
By combining both medical and lifestyle approaches, individuals with Atopic Dermatitis Eczema can effectively manage their condition and experience relief from symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized treatment recommendations and guidance.
Conclusion
Atopic Dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact their quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors associated with Eczema is crucial for early detection and effective management.
It’s important to note that Atopic Dermatitis is just one form of eczema, and there are other types as well. However, what sets Atopic Dermatitis apart is its association with other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever. It’s vital to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Preventing Atopic Dermatitis Eczema flare-ups involves a combination of avoiding triggers and adopting a regular skincare routine. Some preventive measures include keeping the skin moisturized, avoiding harsh soaps and detergents, wearing breathable clothing, and practicing stress management techniques. It’s also essential to identify and avoid any allergens that may worsen the symptoms.
By staying informed, implementing preventive measures, and seeking medical guidance, individuals with Eczema can effectively manage their condition and improve their overall well-being. Remember, early intervention and proactive care are key in minimizing flare-ups and enhancing the quality of life for those living with Atopic Dermatitis Eczema.
FAQ
<div><h3>What is atopic dermatitis eczema?
It is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, itching, and redness of the skin. It is a form of eczema that is often genetic and commonly occurs in individuals with a family history of allergic conditions such as asthma or hay fever.
What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis eczema?
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis eczema</b> can vary, but commonly include dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Other symptoms may include red or brownish-gray patches, small raised bumps, thickened or scaly skin, and skin that may crack or ooze.
What are the causes and risk factors of atopic dermatitis eczema?
The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain triggers such as allergens, irritants, stress, and changes in temperature can worsen symptoms. Additionally, individuals with a family history of atopic dermatitis or other allergic conditions are at a higher risk of developing the condition.
How can atopic dermatitis eczema be managed and treated?
Managing and treating eczema involves a multifaceted approach. It includes avoiding triggers, moisturizing the skin regularly, using prescribed topical medications or ointments, taking oral medications for severe cases, and adopting a healthy lifestyle by maintaining a balanced diet and managing stress levels.
What is the difference between atopic dermatitis and other forms of eczema?
Atopic diseases run in families, and individuals with this history often develop atopic dermatitis, a specific type of eczema linked to allergies. On the other hand, other forms of eczema can develop due to various triggers such as irritants or contact allergens.
How to prevent atopic dermatitis eczema flare-ups?
Take steps to minimize flare-ups of atopic dermatitis eczema, although it cannot be completely prevented. . These include identifying and avoiding triggers, regularly moisturizing the skin, using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products, practicing stress management techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking timely medical treatment and advice.