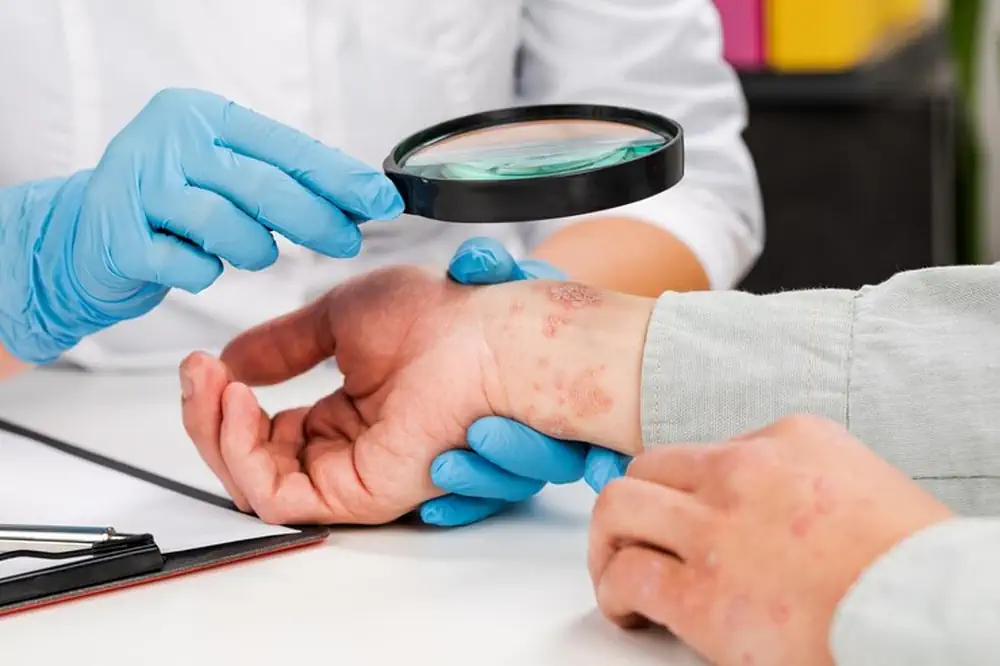
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed, and dry patches of skin. It can affect individuals of any age, though it is most prevalent in children. This article explores the various aspects of eczema, including its symptoms, causes, and how it can be managed and treated.
Key Takeaways
- Eczema is a chronic skin condition that primarily causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin patches.
- There are several types of eczema, with atopic dermatitis being the most common.
- Genetic and environmental factors and immune system responses play significant roles in causing eczema.
- Management and treatment of eczema vary with age and include home remedies and medical interventions.
- Regular skin care and lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms and prevent eczema flare-ups.
Understanding Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis

What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It primarily affects children but can persist into adulthood or start at any age. The condition is not contagious but can significantly impact the quality of life.
Common Symptoms
The hallmark symptoms of eczema include persistent itching and dryness, red or brownish-gray patches, and small, raised bumps that may leak fluid when scratched. Over time, repeated scratching can lead to thickened, cracked, or scaly skin.
Long-term Impact
Eczema’s chronic nature means it can have a lasting impact on patients, often leading to sleep disturbances and emotional distress. Managing symptoms effectively is crucial to improving life quality and preventing long-term skin damage.
Types of Eczema
Eczema encompasses a variety of inflammatory skin conditions, each with distinct triggers and symptoms. Understanding the different types is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Atopic Dermatitis
Often referred to simply as eczema, atopic dermatitis is the most prevalent form, affecting over 7% of American adults. It typically begins in childhood and may be associated with other allergic disorders like asthma and hay fever.
Contact Dermatitis
This type arises from direct contact with irritants or allergens. It is characterized by red, inflamed skin which can be triggered by a variety of substances, from soaps to certain fabrics.
Other Variants
Eczema also includes less common types such as dyshidrotic eczema, which involves blisters on hands and feet, and nummular eczema, known for its round patches of irritated skin. Each type has its specific triggers and symptoms, making it essential to identify the correct variant for proper treatment.
Causes of Eczema

Genetic Factors
Eczema often runs in families, suggesting a strong genetic component. Individuals with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are more likely to develop the condition themselves. This genetic predisposition increases the likelihood of an abnormal skin barrier, which is crucial in protecting against irritants and allergens.
Environmental Triggers
External factors play a significant role in triggering eczema flare-ups. Common environmental triggers include irritants such as soaps and detergents, allergens like pollen and pet dander, and extreme weather conditions. Recognizing and avoiding these triggers can help manage symptoms effectively.
Immune System Response
The immune system’s overreaction to harmless substances can lead to eczema. This hyperactive immune response results in inflammation, causing the skin to become red, itchy, and inflamed. Managing stress and avoiding known allergens are key strategies in controlling this immune response.
Managing Eczema in Different Age Groups

Childhood Eczema
Eczema is most prevalent in children, often manifesting before the age of 5. Many children may outgrow the condition, but it can persist into adolescence and beyond. Effective management includes gentle skincare routines and avoiding known irritants.
Adult Eczema
Adults may experience more persistent and severe forms of eczema. The condition often appears in skin creases such as elbows and knees and can cover extensive areas. Treatment strategies often involve prescription medications and careful skin care.
Elderly Skin Care
As we age, skin naturally becomes drier and thinner, making elderly individuals susceptible to eczema flare-ups. Emphasizing moisturization and avoiding harsh soaps are crucial in managing eczema in the elderly.
Treatment Options for Eczema

Home Remedies
Home remedies play a crucial role in managing eczema symptoms. Moisturizing regularly with products that are hypoallergenic and free of fragrances and dyes can significantly alleviate discomfort. Additionally, natural remedies such as oatmeal baths and coconut oil applications can soothe the skin.
Prescription Medications
A variety of prescription medications are available to treat eczema. Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. Other options include phosphodiesterase inhibitors and immunosuppressants like methotrexate and azathioprine. For severe cases, biologic drugs may be recommended.
Advanced Therapies
Advanced therapies for eczema include phototherapy, which uses ultraviolet light to reduce symptoms, and newer treatments like injectable biologics. These options are typically considered when traditional treatments are not effective.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the severity and type of eczema.
Lifestyle and Home Care

Daily Skin Care Routines
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine is crucial for managing eczema. Daily moisturizing with hypoallergenic products can prevent dryness and reduce flares. It’s also important to use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and avoid hot water during showers or baths.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may help manage eczema symptoms. Foods like fatty fish, leafy greens, and fruits are beneficial. Additionally, some individuals might find relief by identifying and avoiding food allergens that trigger eczema symptoms.
Stress Management
Managing stress is a key component in controlling eczema. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can significantly reduce stress levels. Engaging in these activities regularly can help minimize the frequency and severity of eczema flares.
When to Seek Medical Advice

Symptoms Worsening
If you notice that your eczema symptoms are progressively getting worse, despite following prescribed treatments, it’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider. This includes increased redness, swelling, or pain, as well as the appearance of blisters or oozing that suggests an infection.
New symptoms
Should new symptoms arise, such as severe pain, fever, or an unexpected rash, immediate medical attention is necessary. These could indicate an infection or an allergic reaction that requires prompt intervention.
Regular Check-Ups
Even if your eczema is under control, regular check-ups with a dermatologist are essential. They help ensure that your management plan is effective and adjust treatments as needed. This proactive approach can prevent flare-ups and complications.
Note: Always keep track of any changes in your symptoms and discuss them during your appointments.
Preventing Eczema Flares

Identifying Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial in preventing eczema flares. Common triggers include allergens, irritants, and environmental factors. Keeping a detailed diary of flare-ups can help pinpoint specific triggers.
Moisturizing Techniques
Effective moisturizing is essential to maintain skin barrier function and prevent dryness. Apply moisturizers immediately after bathing to lock in moisture. Choose products that are free from fragrances and irritants.
Clothing and Fabrics
Selecting the right clothing and fabrics can significantly reduce eczema symptoms. Opt for soft, breathable materials like cotton and avoid rough, scratchy fabrics. Regularly washing new clothes before wearing them can also help minimize irritation.
Note: Managing eczema effectively also involves being aware of other related conditions, such as asthma symptoms, which can exacerbate skin issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, eczema, particularly atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent and complex skin condition that affects millions worldwide. While there is no cure, understanding the symptoms, triggers, and various types of eczema can significantly aid in managing the condition effectively. Treatments ranging from home remedies to prescription medications are available to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Individuals must work closely with healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that suits their specific needs and to stay informed about new research and therapies that could offer further relief.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as Atopic Dermatitis, is an inflammatory skin condition characterized by itchy, dry, and cracked patches of skin. It’s common in children but can occur at any age and is chronic with periodic flares.
What are the common types of Eczema?
The main types of eczema include Atopic Dermatitis, Contact Dermatitis, Dyshidrotic Eczema, Hand Eczema, Neurodermatitis, Nummular Eczema, and Stasis Dermatitis.
What causes Eczema?
Eczema is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It involves an overactive immune response to irritants or allergens and is often linked to other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever.
How can Eczema be treated?
Treatment options for eczema include home remedies, over-the-counter treatments, prescription medications, and advanced therapies like injectables. Regular skin care and avoiding triggers are also crucial.
Can diet and lifestyle changes help manage Eczema?
Yes, maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and adopting a daily skincare routine can help control eczema symptoms and reduce flare-ups.
When should someone with Eczema seek medical advice?
Medical advice should be sought if eczema symptoms worsen, new symptoms appear, or the condition does not improve with home treatment. Regular check-ups are also recommended to manage the condition effectively.